

Arizona printers with the White Ink Option provide under-printing for non-white media or objects, over-printing for backlit applications on transparent media and/or printing white as a spot color.
When working with white ink there are three data layers available that allow you to determine the area the white ink will cover and also how it will appear (or not appear) in relation to other colors, depending on the layer it is placed in. You can determine the density of the white ink by altering the drop size. The layer setup is defined in the media model but can be modified as a job printer setting within the ONYX software. When the white ink information is properly prepared according to the methods described in this chapter and the print job is sent from the ONYX software (ONYX Thrive) to the printer, you have an opportunity to verify that the layers are properly embedded in the job.
With the white ink print job selected in the Job Control module of the printer software, click the Layers button to activate a graphical representation of the Print Layers that allows you to verify the layer order.
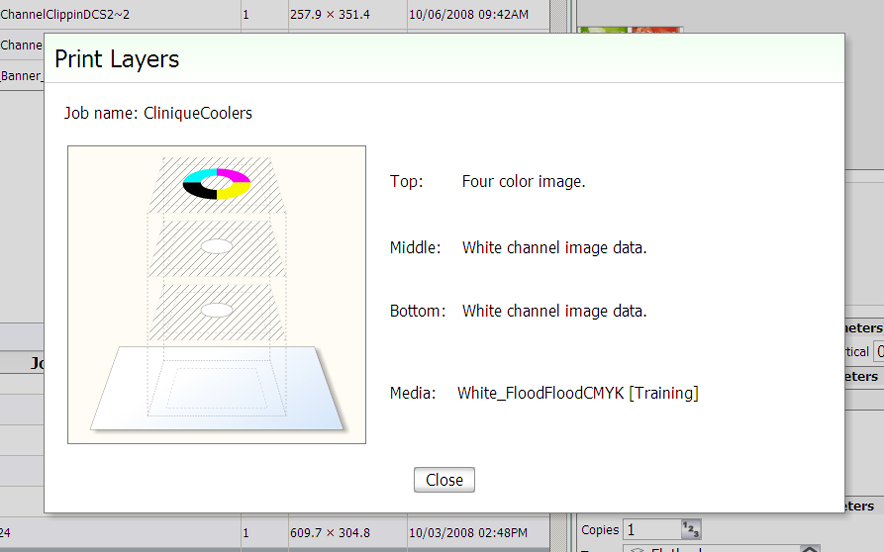 Preview Layer in Printer UI
Preview Layer in Printer UI |
White ink can be printed using flood fill data generated by the printer or job spot data. A printer flood fill cover the whole image area while spot data is assigned in specific areas. Job data is separated by the ONYX software into six data planes: C, M, Y, K, Spot 1, and Spot 2. The white ink channels are usually configured to print using the Spot 1 or Spot 2 data plane or a printer flood fill, but can also be printed using the C,M,Y or K data plane.
White ink print job output can be accomplished in a variety of ways depending on the desired results and preferred working process. There are three primary methods and they can be used either independently or all at the same time. The workflow options are:
Printer Flood Fill Layer Configuration,
ONYX software Spot Layer Tool, and
White Spot Data Image Preparation.
Printer Flood Fill Layer Configuration in an ONYX workflow does not require any pre-rip file preparation and is the easiest method of achieving white ink output. All that is required is to set up the Layer Configuration to include a printer flood layer. The printer flood layer encompasses the bounding box (the outer border of the image) of the file being processed. There is also an option to control the amount of flood by choosing the drop level. The higher the drop level number the greater the amount of white ink.
ONYX Software Spot Layer Tool offers many options to process an image, and thus allows various possible configuration choices. You can save these configurations as Filters and place them in a Quick Set and this makes it possible to re-create with minimal effort settings that are often used. All work with the Spot Layer tool requires an ONYX media profile with at least one spot color.
White Spot Data Image Preparation requires that the white data be prepared in image editing programs such as Adobe Illustrator®, InDesign, or PhotoShop®. You must use specific naming conventions and image use protocols in order for the ONYX RIP-Queue software to process the data as desired. This method may be the best choice if the desired white ink spot data includes complicated selections or if data is being created for outsourcing. A reasonable level of proficiency in these programs is recommended to use this technique.
All of these methods can also be used either alone or in conjunction with each other to create the desired output results. For example, you may generate the spot layer information for parts of an image in PhotoShop and then go on to specify a Flood Layer Configuration in ONYX Thrive. This can result in a Flood Layer and a Spot Layer followed by a CMYK Layer. The spot data and the flood will occupy two layers of white density and the CMYK image data can occupy the third layer. You can determine the print order of these layers in ONYX Thrive.
Layers can be defined at any of the following locations:
Defined in the media when the media is created - Mode Options
Selected in a Quick Set - Media Options
Modify the printer settings of a processed job in RIP Queue - right-click the job, edit printer settings.
You are not required to use layers when you print white spot data. It can also be printed with print modes other than Quality-Layered.
The following are some specific examples of the ways that the white ink workflow can be applied.
|
Application |
Bottom |
Middle |
Top |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Backlit First Surface (printing on the front side of the media) |
White |
CMYK |
CMYK |
CMYK layers contain same data. |
|
Backlit Second Surface (printing on the back side of clear media) |
Reverse printed CMYK |
Reverse printed CMYK |
White |
|
|
Day-Night (First or Second surface) |
CMYK |
White |
CMYK |
CMYK data is reversed or right-reading |
|
Opaque |
White |
White |
CMYK |
3 layers |
|
Opaque |
<empty> |
White |
CMYK |
2 layers |
Backlit Application
The backlit application involves printing onto a transparent or translucent material and mounting the finished piece onto a light box or location where illumination from behind is possible. In the backlit application, white ink is intended to provide a light diffusing layer. This application is possible using either 2 or 3 layers.
Day-Night Application
Similar to backlit, the day-night application also involves printing onto a transparent or translucent material. A day-night print can be viewed either front-lit or backlit. This is achieved by printing color data on two separate layers with a white diffusing layer in the middle.
Opaque Application
The opaque application involves printing CMYK data onto non-white media. For this application, white ink is required both to enable the printer to produce images where white forms part of the image content, as well as to act as a base for the CMYK color set.