

The licenses are based on a MAC address of the computer where the Floating License Server (FLS) is installed. A MAC address is the unique identifier of a network adapter. A computer may have multiple network adapters, both physical and virtual (Ethernet, Wi-Fi, VPN, VMplayer, …). The FLS manages the licenses. The licensed application (PRISMAprepare and/or PRISMAdirect) must connect to the FLS. Therefore, you have to specify:
The name of the FLS. The server name can be a network name or an IP address. You have to specify the server name in the licensed application.
The port of the FLS. You have to specify the license server port in both the licensed application and the [License Server Administration].
Content of this article
Configure the ports for the license server
Check the port numbers of the license server and the licensed application
PRISMAprepare: check the IP address or name of the FLS
PRISMAdirect: check the IP address or name of the FLS
Terminology
FLS: the computer where the Floating License Server is installed.
Licensed application: PRISMAprepare and/or PRISMAdirect
Open the [License Server Administration].
Select [License server settings] and click [Edit] .
Click [Edit ports].
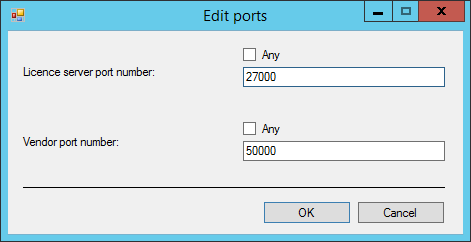
The license server port
The licensed application uses this port number to initiate communications with the FLS. The lmgrd.exe process listens on the license server port.
Range: [27000 - 27009] or [Any].
If the port number is [Any], the FLS uses the first available port in the range [27000 - 27009] to listen for the licensed application. The licensed application tries to connect to the FLS starting with port 27000. If the FLS does not respond, the licensed application tries the next port. When all ports in the range [27000 - 27009] are blocked or in use by other applications, the licensed application cannot connect to FLS.
The vendor port
When the licensed application connects to the license server port, it receives the vendor port number from the FLS. Then, the licensed application opens the vendor port. The ocelmgrd.exe process listens on the vendor port.
Range: [49152 - 65535] or [Any].
If the port number is [Any], the first available port in the range [49152 - 65535] is used by the FLS and the licensed application.
The FLS uses TCP/IP ports to communicate with the licensed application. You have to check if the same license server port is used in both the [License Server Administration] and the licensed application.
To check the license server port for the FLS in PRISMAprepare, do:
Open the [PRISMAprepare Administration].
Select [Licenses] and double-click [Licenses] in the right-hand pane.
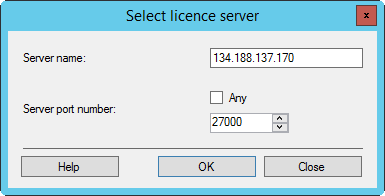
Click [Select license server].
The "Server port number" must be equal to the "License server port number" in the [License Server Administration].
To check the license server port for the FLS in PRISMAdirect, do:
Open the [Configuration] workspace.
Click [System] and select [License].
The "Port" number must be equal to the "License server port number" in the [License Server Administration].

Check the TCP/IP ports used by the FLS:
Open the [License Server Administration].
Select [License server settings] and click [Edit] .
Click [Edit ports].

Troubleshooting
Using value [Any] allows for dynamic assignment of a port number. Using a dynamic port allows the licensed application to adapt itself to changing configurations. However, creating a connection dynamically also costs time in retries, hang-ups, and timeouts. Furthermore, a firewall can allow only fixed ports and block dynamic ports. Use a fixed port for:
The license server port, for example, 27000. Configure this port in both the [License Server Administration] and the licensed application.
The vendor port, for example, 50000. Configure this port in the [License Server Administration].
When you want to use a fixed port, you must be sure that the selected port can be used:
Check that:
The FLS can open the license server port for listening.
The licensed application can open the vendor port.
If a port cannot be opened, an error appears in the log file lmgrdFile.log. Location of the log file: C:\Program Files (x86)\Oce\Floating License Server\lmgrdFile.log
Check that the licensed application can connect to the FLS. For example:
The firewall can block access to the fixed port. You have to configure the firewall.
Other applications use all ports in the range [27000 - 27009]. You have to free one port in the range [27000 - 27009].
The FLS name can be a network name or an IP address. To check the name of the FLS, do:
Open the [PRISMAprepare Administration].
Select [Licenses] and double-click [Licenses] in the right-hand pane.
Click [Select license server].
Local Floating License Server
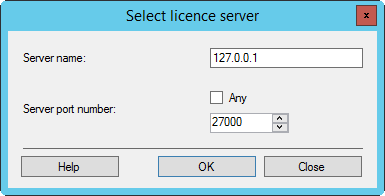
The FLS and the licensed application are installed on the same computer. Use the following FLS name:
127.0.0.1
This is the IP address of the local host.
Do not use: "localhost", the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or a short DNS name.
Remote Floating License Server
The FLS and the licensed application are installed on different computers. Use the following FLS name:
The fixed IP address
It is recommended to use the fixed IP address of the FLS.
Troubleshooting
If the connection is lost while you use a fixed IP address for the FLS:
Check whether the IP address of the FLS has changed. Update the IP address in the licensed application. The following screenshot uses 134.188.137.170 as IP address. You have to use the actual IP address of your FLS.

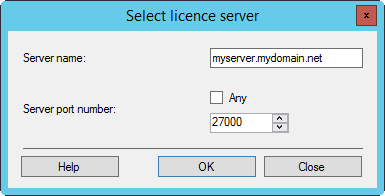
The Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN), for example, myserver.mydomain.net.
Use the FQDN if the FLS does not have a fixed IP address. For example, the DHCP server assigns a dynamic IP address to the FLS.
Troubleshooting
If the licensed application using an FQDN cannot connect to the FLS:
The DNS server must know the FLS else the FLS cannot receive the dynamically generated IP address from the DHCP server. This DNS server must also be known by the licensed application.
Ping the FQDN to check if it is already resolved by the DNS server.
Do not use: a short DNS name, for example, myserver. When using a short DNS name, the licensed application must try all known domain names to find or fail to find the FLS.
The FLS name can be a network name or an IP address. To check the name of the FLS, do:
Open the [Configuration] workspace.
Click [System] and select [License].
Local Floating License Server
The FLS and the licensed application are installed on the same computer. Use the following FLS name:
127.0.0.1
This is the IP address of the local host.
Do not use: "localhost", the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or a short DNS name.

Remote Floating License Server
The FLS and the licensed application are installed on different computers. Use the following FLS name:
The fixed IP address
It is recommended to use the fixed IP address of the FLS.
Troubleshooting
If the connection is lost while you use a fixed IP address for the FLS:
Check whether the IP address of the FLS has changed. Update the IP address in the licensed application. The following screenshot uses 134.188.137.170 as IP address. You have to use the actual IP address of your FLS.

The Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN), for example, myserver.mydomain.net.
Use the FQDN if the FLS does not have a fixed IP address. For example, the DHCP server assigns a dynamic IP address to the FLS.
Troubleshooting
If the licensed application using an FQDN cannot connect to the FLS:
The DNS server must know the FLS else the FLS cannot receive the dynamically generated IP address from the DHCP server. This DNS server must also be known by the licensed application.
Ping the FQDN to check if it is already resolved by the DNS server.

Do not use: a short DNS name, for example, myserver. When using a short DNS name, the licensed application must try all known domain names to find or fail to find the FLS.