

This topic contains the following instructions.
Change the attributes of the colour preset
Use the [Colour bar] option
Use the [Information bar] option
Use the [Image smoothing] option
Use the [Moiré reduction for images] option
Use the [Trapping] option
Use the [Page numbering] option
 Job properties
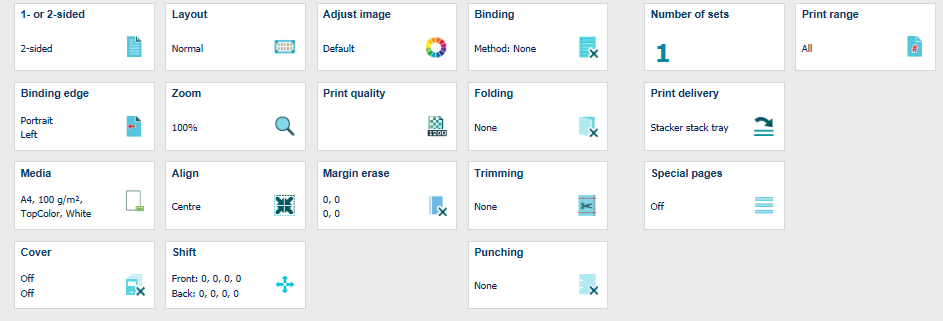
Job propertiesThe job properties depend on the product.
The colour preset attributes define the main colour properties of the job. You can change one or more attributes for your job. In addition, you can save the changed colour preset for later reuse.
Go to the job location and select the job.
Click the edit job button
 .
.
Click [Print quality].
 Print quality options
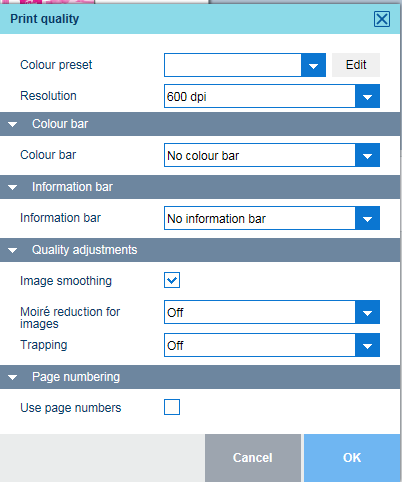
Print quality optionsUse the [Colour preset] drop-down list to select one of the available colour presets.
To edit the colour preset attributes, click [Edit].
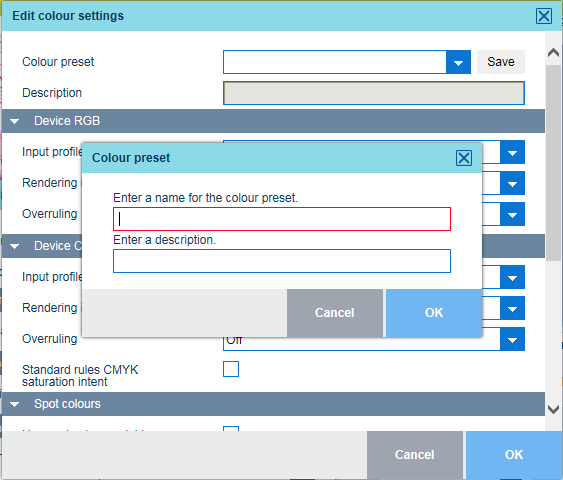
Use the [Input profile] drop-down list to select one of the available DeviceCMYK or DeviceRGB input profiles.
Use the [Overruling] option to indicate if the RGB or CMYK embedded input profile and rendering intent must be overruled or not.
[Off]: no overruling of embedded input profile and rendering intent.
[Intents]: only overruling of embedded rendering intent.
[Profiles and intents]: overruling of embedded input profile and rendering intent.
Use the [Standard rules CMYK saturation intent] option to indicate if the standard ICC colour management rules of the CMYK saturation intent must be applied. For the CMYK saturation intent, the printer by default maps pure (100%) C, M, Y and K input colours into pure C, M, Y and K output colours. However, it can be required that the standard ICC colour management rules must be used without an improvement of the colour management of the printer.
Use the [Spot colour matching] option to enable or disable spot colour matching. If a source file contains a spot colour, the printer must know the spot colour definition to exactly print the required colour.
If the [Spot colour matching] option is enabled, you can select a colour mapping group. With colour mapping you can re-define the colour values of a source colour (RGB, CMYK or spot colour).
Use the [Print black & white] option to define how jobs are printed: in black & white or in colour.
Use the [PDF overprint simulation] option to make opaque objects look transparent. Underlying objects become visible. If this option is disabled, the colours on top will knock out all underlying colours.
Use the [Use PDF/X output intent] option to indicate if PDF source files are printed according to their embedded output intent. PDF/X specifies the printing conditions for which a PDF/X file is created. These printing conditions are called output intents. The printer can handle PDF/X compliant PDF source files. Then, the output intent overrules the DeviceCMYK rendering intent and DeviceCMYK input profile.
Use the [Overprinting black] option to force the printer to print pure black text and graphics over the background colour. The [Overprinting black] prevents that white lines appear around black characters and graphics.
[As in document]: overprinting black is not applied.
[Enabled for text]: overprinting black is applied to texts.
[Enabled for text and graphics]: overprinting black is applied to texts and graphics.
Use the [Preserve pure black] option to apply pure black preservation when possible. Pure black preservation means that the colour black is composed of 100% K ink. When pure black preservation is not possible or disabled, the colour black is composed of a mixture of two or more C, M, Y, and K inks.
Use the [Black Point Compensation (BPC)] option applies to the relative colorimetric rendering intent. Details in dark regions of the document can be lost with the standard colour conversion. The Black Point Compensation aligns the darkest level of black achievable (black point) of the source to the darkest level of black achievable on the printer.
[Disabled]: Black Point Compensation is not applied.
[Adobe BPC]: the Adobe implementation of [Black Point Compensation (BPC)].
[Enhanced BPC]: when the black point in the document is rather light, select [Enhanced BPC].
When you want to save the changes in a colour preset, click [Save] and enter a name.
 Colour settings
Colour settingsClick [OK] to save the changes for the job.
When you want to print a colour bar, select one of the available colour bars.
Use the [Colour bar] drop-down list to select the required colour bar.
Click [OK] to save the changes.
When you want to print a colour bar, select one of the available colour bars.
Use the [Information bar] drop-down list to select the required information bar.
Click [OK] to save the changes.
Expand the [Quality adjustments] option group.
Use the [Image smoothing] option to prevent unsmooth lines and image blocks in the document. This occurs when source objects have a lower resolution than the printer. The [Image smoothing] interpolation method only affects images below 300 dpi.
Click [OK] to save the changes.
Expand the [Quality adjustments] option group.
Use the [Moiré reduction for images] option to apply a Moiré reduction algorithm to enhance photographic images. Please note that when images have a resolution below 300 dpi, the Moiré reduction only takes effect when the [Image smoothing] option is enabled.
Click [OK] to save the changes.
When you want to improve the object registration, you can select one of the available trapping presets or create a new trapping preset.
Expand the [Quality adjustments] option group.
Use the [Trapping] drop-down list to disable the trapping or to select one of the available trapping presets.
Click [OK] to save the changes.
The default font and the font size are predefined.
Use the [Page numbering] check box to indicate the use of page numbers.
Click [OK] to save the changes.