

With [PRISMAguide XL] you can create multi-layered print jobs without having to go through extensive preprocessing in Adobe Photoshop or Adobe Illustrator. You don't need to name the spot colors in a specific way, or ensure that white data layers are on top, or have overprint enabled.
To use white ink or gloss in applications, a CMYKSS profile and a specific resolution is needed. You can download the profiles on graphiplaza.cpp.canon.
Check / select the settings for:
[Preset]
[Media]
[Resolution]
[Mode]
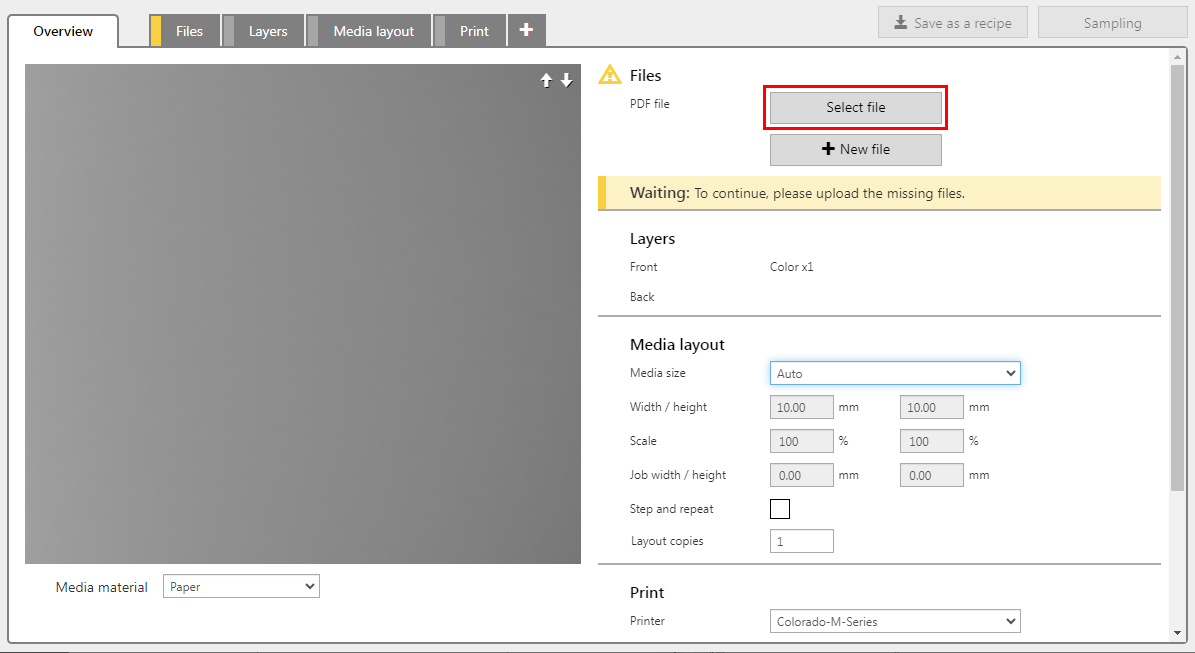
If you need more source files, click [New file].
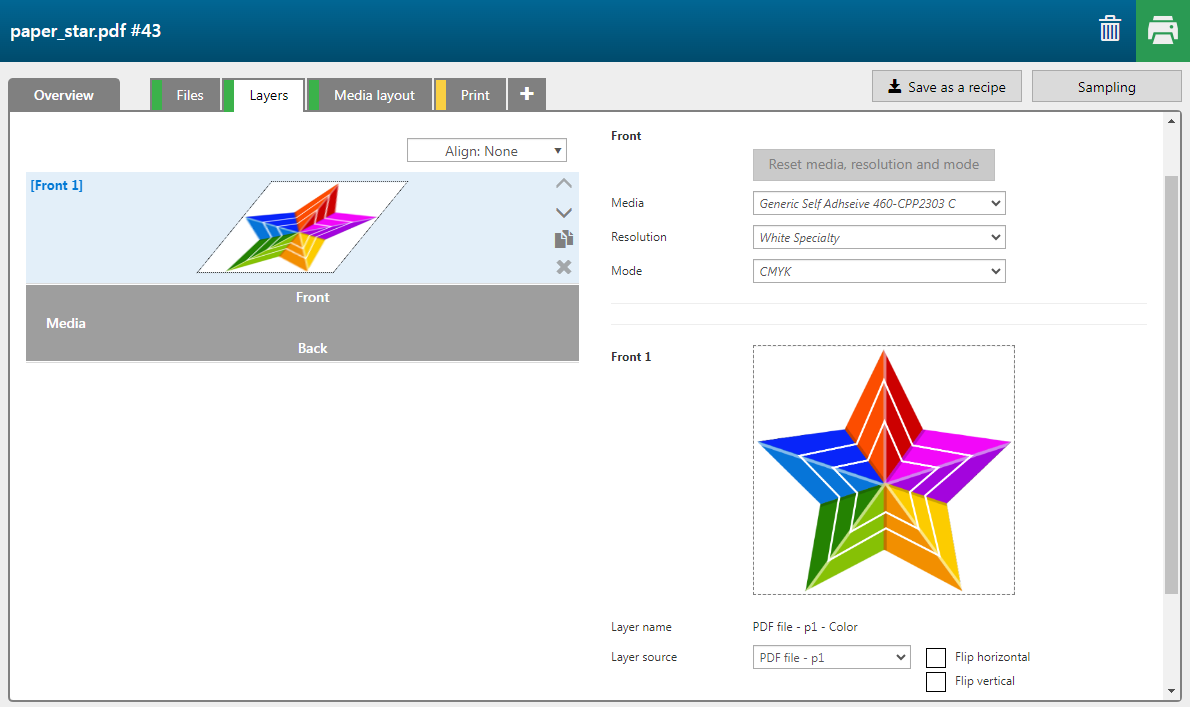
For this example, we want to create more layers. Click four times on the duplicate button.

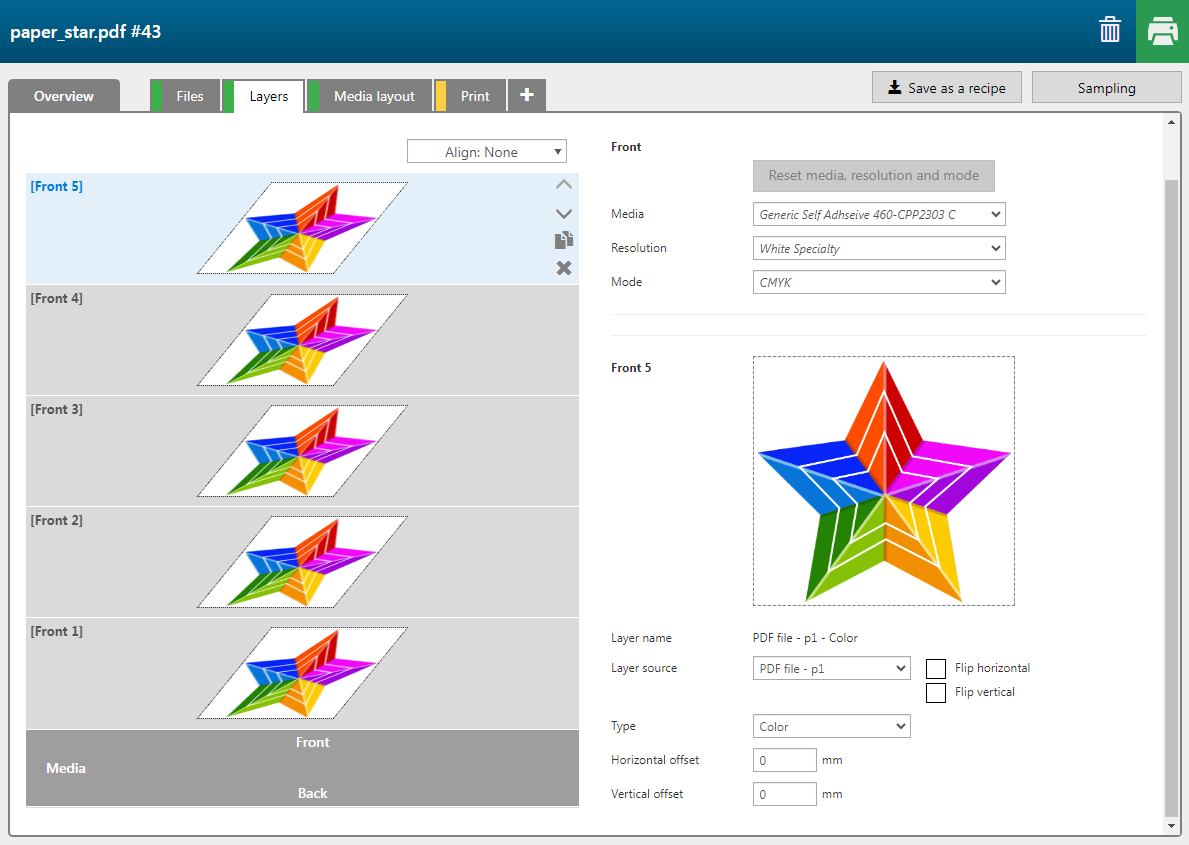
Open the [Layer source] drop-down list to assign pages, layers or spot colors, present in the input file(s) as input to a print layer.
Change the order of the layers, if necessary, by dragging or by using the icons.
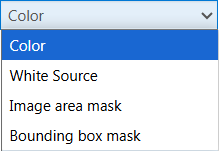
Color layers are printed in CMYKW, White source layers are printed in white only.The mask layers can be printed in [White], [Block-out (black)] and [Gloss] or a [Custom color].
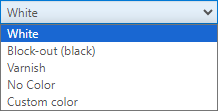
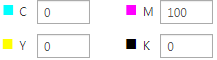
[Custom color], allows you to enter CMYK values to specify the color of the mask.
There are two types of mask layers:
[Bounding box mask]
The shape of the mask layer is a rectangle in the size of the image. Parts in the media color are part of the layer, as well as the parts that are transparent.
[Image area mask]
The mask detects the color data of the image and leaves out the parts that are in the media color. A pixel (in a raster image) and vector data in the media color will be set to transparent.
Vector data will be rasterized. Except when you enable the function: [Keep vector data] . Then the vector data will not be transparent and will be part of the [Image area mask] layer.
[Max raster DPI]
To keep large print jobs manageable, you can define the DPI for the mask layers. The [Actual DPI: {0}] shows the maximum DPI depending on the size of the layer. You can set the value lower but not higher. When you do, the higher value will be disregarded.
400 DPI - 1.625 * 1.3 m (2.11 sqm)
300 DPI - 1.625 * 2.3 m (3.73 sqm)
200 DPI - 1.625 * 5 m (8.125 sqm)
100 DPI - 1.625 * 21 m (34.125 sqm)
50 DPI - 1.625 * 40 m (65 sqm)
<50 DPI - not supported
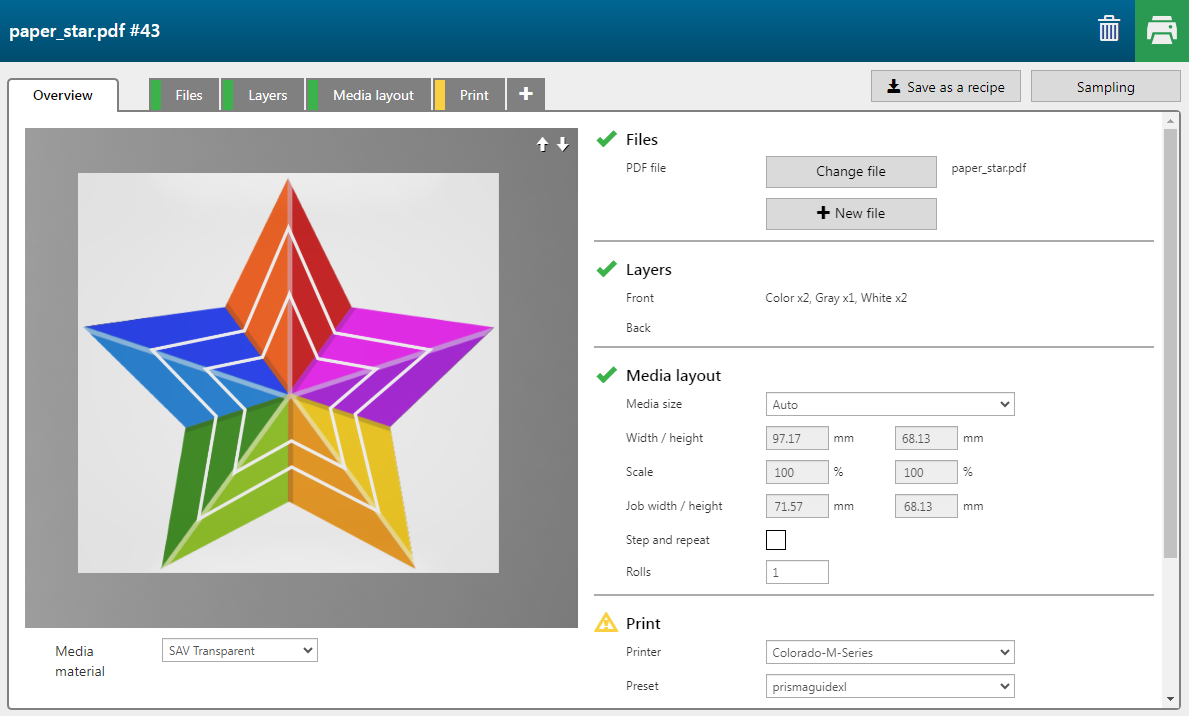
A design can contain raster and vector data in one. In this example the image is a raster image combined with vector data (white lines in the star).
[Threshold]
The [Threshold] function determines how close the color values should be to the set media color. These pixels will also be set as media color and are made transparent in the [Image area mask] layer. The higher the number the higher the tolerance.
Media color
Default the media color is set to white. You can select a different media color. This color will be set to transparent in the [Image area mask] layer.
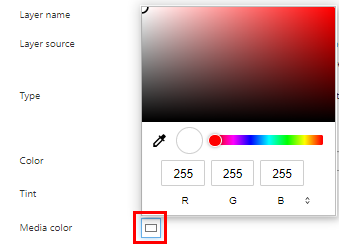
[Fill choke/spread]
To prevent that a [Block-out (black)] layer or [White] layer is visible in the top layers, you can change the [Fill choke/spread] values.
Change the value to make the mask area smaller (Choke) or larger (Spread). A positive value makes the area slightly smaller, a negative one makes the area slightly larger.
|
Layer |
[Layer source] |
[Type] |
Remark |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
[Front] 5 |
2 pages PDF - p1 |
[Color] |
The layer is printed in CMYK. |

|
|
[Front] 4 |
2 pages PDF - p1 |
[Image area mask] [Color]: [White] |
The layer is printed in white. [Keep vector data]: Yes |
|
|
[Front] 3 |
2 pages PDF - p1 |
[Image area mask] [Color]: [Block-out (black)] |
The layer is printed in a combination of black and white. [Keep vector data]: No [Fill choke/spread]: 4 |
|
|
[Front] 2 |
2 pages PDF - p1 |
[Image area mask] [Color]: [White] |
The layer is printed in white. [Keep vector data]: Yes |
|
|
[Front] 1 |
2 pages PDF - p2 |
[Color] |
The layer is printed in CMYK. |
You can rotate, shift, or zoom in and out on the preview as follows:
Rotate: click and hold the left mouse button.
Shift: click and hold the right mouse button.
Zoom in and out: rotate the mouse wheel.
In the preview you can check if the back image must be flipped, which can be the case when texts are visible. In this case this is not needed.
See for more information:
See for more information: The Print tab

If you want to save an application as a recipe for future use, see Save an application as a recipe.