

A transaction setup with the status [Opened], can be adjusted.
Open the Settings Editor and go to: .
 [Transaction setups] tab
[Transaction setups] tabCheck that the transaction setup you want to change has the status: [Opened].
Click the [IPDS transaction setup] tab.
 [IPDS transaction setup] tab
[IPDS transaction setup] tabChange the settings one by one or click [Edit] in the title bar to adjust the settings of a group in one dialog.
Validate the transaction setup.
Make sure that you reload a transaction setup that is active when you make the changes.
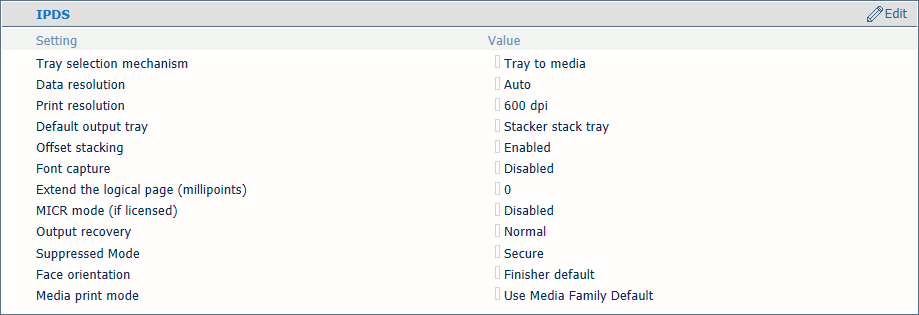 IPDS transaction setup settings
IPDS transaction setup settings|
[IPDS] settings |
Description |
|---|---|
|
[Tray selection mechanism] |
A transaction printing job always uses the media definitions as specified in Settings Editor. Select [Tray to tray] or [Tray to media]. The IPDS data stream contains a reference to a logical tray. There are 36 logical trays that can be assigned to a physical paper tray ([Tray to tray] ) or to media of the media catalog ([Tray to media] ). |
|
[Data resolution] |
Select the resolution of the bitmaps the printer accepts. |
|
[Print resolution] |
This setting defines the IPDS print resolution. |
|
[Default output tray] |
Select the default output tray. |
|
[Offset stacking] |
Select if stacking occurs with or without an offset. |
|
[Font capture] |
Indicate if fonts and other resources can be captured to the printer disk. |
|
[Extend the logical page (millipoints)] |
When you want to print with a slightly larger page size, you can increase the logical page size with the entered number of millipoints (unit of angle measurement). |
|
[Output recovery] |
Use this setting to keep the printed output according to the original source. First select [Suppressed], and then use the [Suppressed Mode] mode to select [Secure]. |
|
[Face orientation] |
Select the delivery orientation in the output tray: [Face up] or [Face down]. |
|
[Media print mode] |
Select the media print mode of the transaction setup. Ensure the selected media print mode matches all media definitions the transaction setup uses for the tray selection mode. The setting [Use Media Family Default] refers to the default media print mode of the media family. 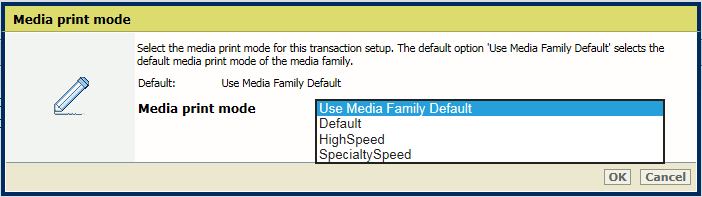 IPDS media print mode
IPDS media print mode |
You link logical trays (indicated by a number from 1 to 36) to media of the media catalog. The printer maps the logical tray to the physical paper trays that hold these media. The schedule shows the media the job uses.
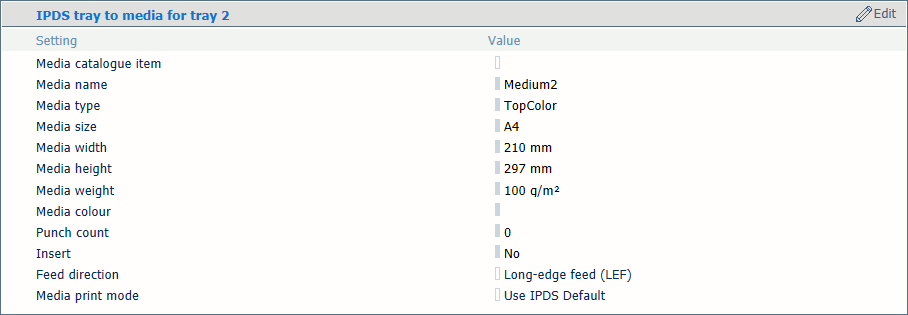 Media selection for tray-to-media mode
Media selection for tray-to-media modeUse the [Media catalog item] setting to select media from the media catalog.
Use the [Feed direction] setting to select the feed direction of the media.
Use the [Media print mode] setting to select the media print mode of the selected media. The option [Use IPDS Default] refers to the [Media print mode] setting in the list of IPDS settings.
Click [Edit] in the title bar to adjust the settings in one dialog.
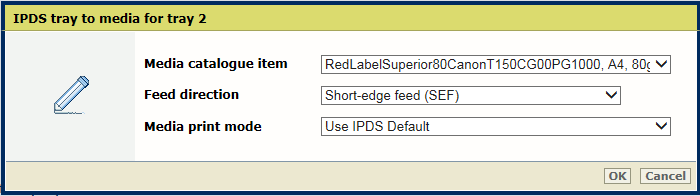 Media selection for tray-to-media mode
Media selection for tray-to-media mode
You link logical trays (indicated by a number from 1 to 16) to physical paper trays. The printer uses media that are assigned to these physical paper trays. The schedule shows the media the job uses.
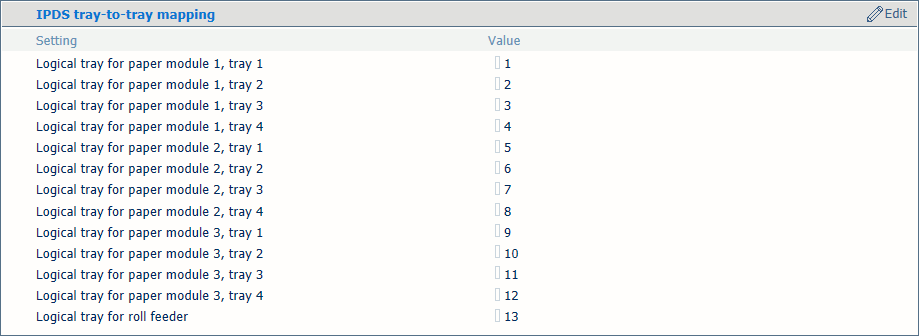 Tray selection for tray-to-tray mode
Tray selection for tray-to-tray modeDefine the logical tray values for all physical paper trays the jobs use.
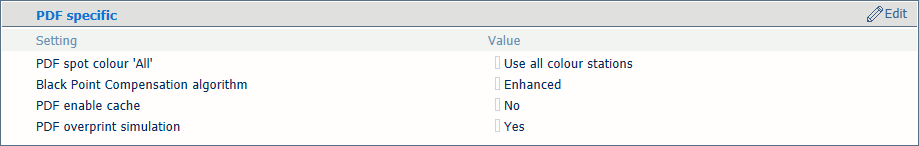 PDF settings
PDF settings|
PDF settings |
Description |
|---|---|
|
[PDF spot color 'All'] |
PDF data can have a number of pre-defined spot colour names. This (exactly spelled) spot color name prints all primary colors instead of the source color. This results in a rich black. |
|
[Black Point Compensation algorithm] |
This setting applies to the relative colorimetric rendering intent. Details in dark regions of the document can be lost with the standard color conversion. The Black Point Compensation aligns the darkest level of black achievable (black point) of the source to the darkest level of black achievable on the printer.
|
|
[PDF enable cache] |
Use this setting to realize that the PDF cache automatically identifies and stores objects that are used more than once in the job. |
|
[PDF overprint simulation] |
Use this setting to make opaque objects look transparent. Underlying objects become visible. If this function is disabled, the colors on top will knock out all underlying colors. |
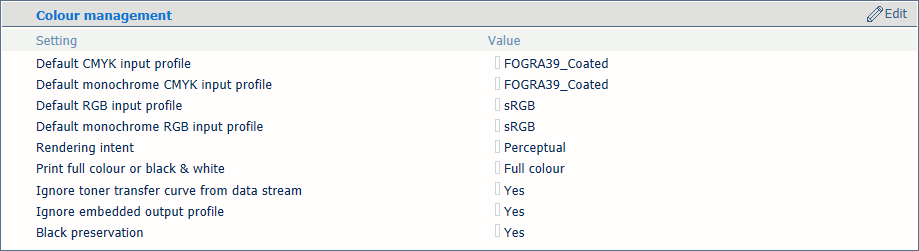 Colour management settings
Colour management settings|
Color management settings |
Description |
|---|---|
|
[Default CMYK input profile], [Default monochrome CMYK input profile], [Default RGB input profile], [Default monochrome RGB input profile] |
Select a default input profile for the four types of input profiles. |
|
[Rendering intent] |
Select the rendering intent. |
|
[Print full color or black & white] |
Use this function to define how jobs are printed: in black & white or in color. |
|
[Ignore toner transfer curve from data stream] |
The printer can use or ignore toner transfer curves that are in the data stream. |
|
[Ignore embedded output profile] |
Use this setting to ignore the RGB or CMYK embedded output profiles. |
|
[Black preservation] |
Use the setting to apply pure black preservation when possible. Pure black preservation means that the color black is composed of 100% K ink. When pure black preservation is not possible or disabled, the color black is composed of a mixture of two or more C, M, Y, and K inks. |
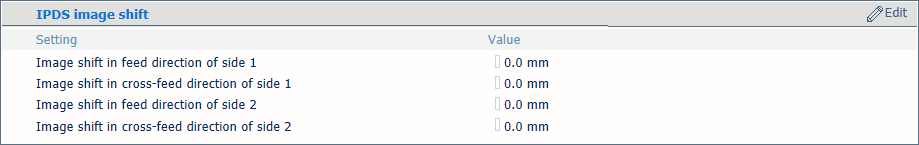 Image shift settings
Image shift settings|
Image shift settings |
Description |
|---|---|
|
[Image shift in feed direction of side 1], [Image shift in cross-feed direction of side 1] |
Use these settings to define the image shift. When you use pre-printed media with marked areas for specific text, misalignments can occur. Also use this setting to better align variable data on pages, such as names or addresses. There are settings for the feed direction and the cross-feed direction in combination with the sheet side. You can also adjust the image shift on the control panel. |
Input trays that contain the same media as the tray defined for the job are automatically linked. This means that when one of the paper trays is empty, printing continues from another paper tray that holds the same media.
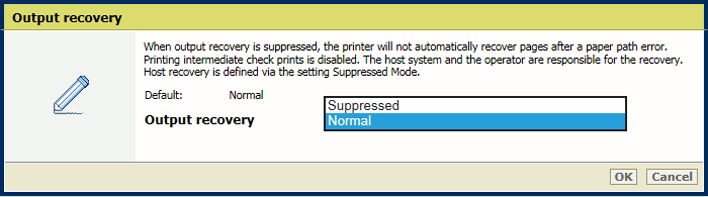 Output recovery
Output recoveryWhen multiple prints for the same source file page are not acceptable, for example in case of printing for lotteries or bank accounts, you can set up a secure output recovery in the transaction setup. Both the printer and the IPDS host can be involved to recover the errors.
Use the table below to choose the recovery behavior.
|
Error recovery modes |
Description |
|---|---|
|
[Normal] recovery |
The printer recovers the output from the point the error occurred, like the printer behavior in the document printing mode. At least one source file page is printed. This may result in double prints. |
|
[Suppressed Mode], [Normal] recovery |
The host recovers the print process from the point the error occurred. This may result in double prints. Intermediate check prints are disabled. |
|
[Suppressed Mode], [Secure] recovery |
The host recovers the print process from the point the error occurred and prevents duplicates. Intermediate check prints are disabled. The printer reports to the host what sheets were affected by the errors. |
 [Color number and color names of cyan color station]
[Color number and color names of cyan color station] You can define custom names or numbers for the color stations.
|
Color station definition |
Description |
|---|---|
|
[Color number] |
When you want to select color stations by using a number, enter a unique value (1-254). The Black color station has the value of zero and you cannot change this number. The other default color numbers are:
|
|
[Color name 1] |
Names are encoded by UTF-16 Unicode. For every color station 6 names can be specified, to enable a color selection by a name. For the cyan, magenta and yellow color stations, the default lists of color names are empty. The literally spelled names 'Gray', 'Cyan', 'Magenta ', 'Yellow ', 'Black ', 'All ', 'None' are reserved for PDF and cannot be used. |