

Output profiles determine how the system will print color. PRISMAsync uses media families to indicate which output profiles will be used to reproduce color on these media.
When the default output profiles do not achieve your color reproduction standards on specific media, you can create new output profiles. The profile accuracy test can help to determine if you need to create new output profiles for the specific media.
The creation of new output profiles can be done during the media family calibration. The embedded color profiler creates and installs an output profile and calibration curve for every halftone. As part of the procedure, you measure the calibration charts printed on the specific media.
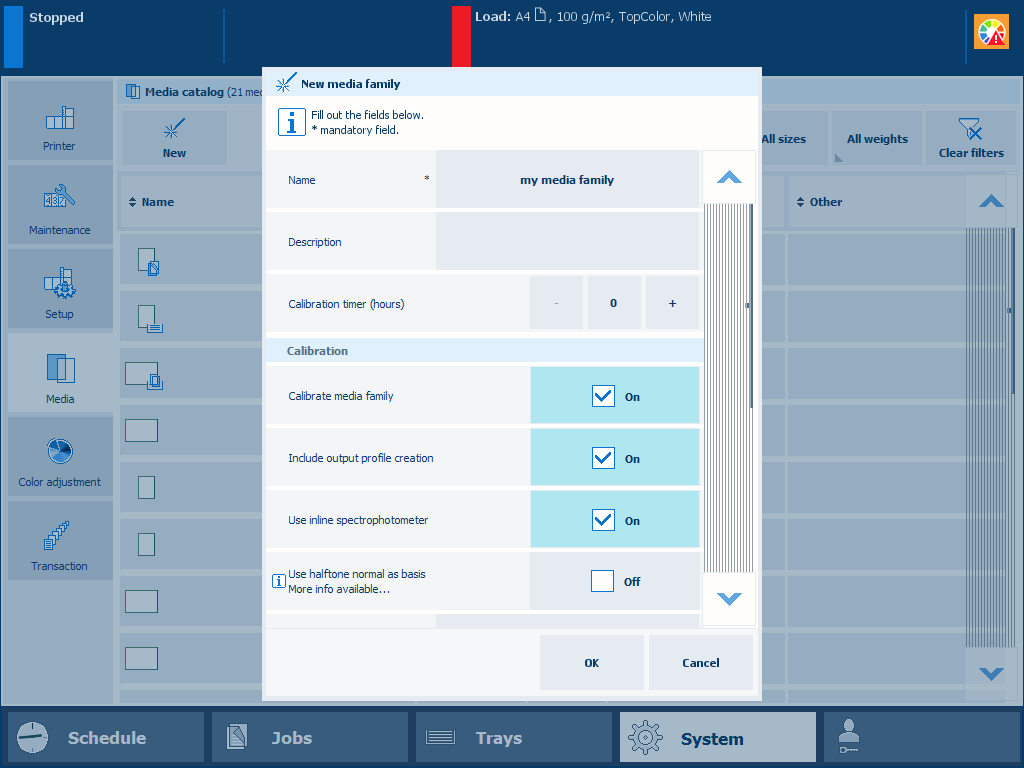 Indicate media family calibration options and output profile creation
Indicate media family calibration options and output profile creationCalibrate the printer.
You must always perform a printer calibration before you continue with this procedure.
Perform a shading correction.
Touch .
Fill out the general media attributes.
For optimal print quality, you must define the correct values for the following media attributes:
Size
Weight
Surface type
Select [Create new media family].
Touch [OK].
Select [Calibrate media family].
Select [Include output profile creation].
Select [Use inline spectrophotometer] if applicable.
You can use the online spectrophotometer with the following media sizes: A3/11 inch x 17 inch, SRA3, 305 mm x 457 mm (12 inch x18 inch), and 330 mm x 483 mm (13 inch x 19 inch).
Select [Use halftone normal as basis] to shorten the media family calibration.
Select the image adjustment, if required.
Load at least 12 sheets of the media for which you create the media family.
Touch [OK].
Follow the instructions on the control panel.
After you created the output profiles, the feedback window shows the results of the performed procedure.
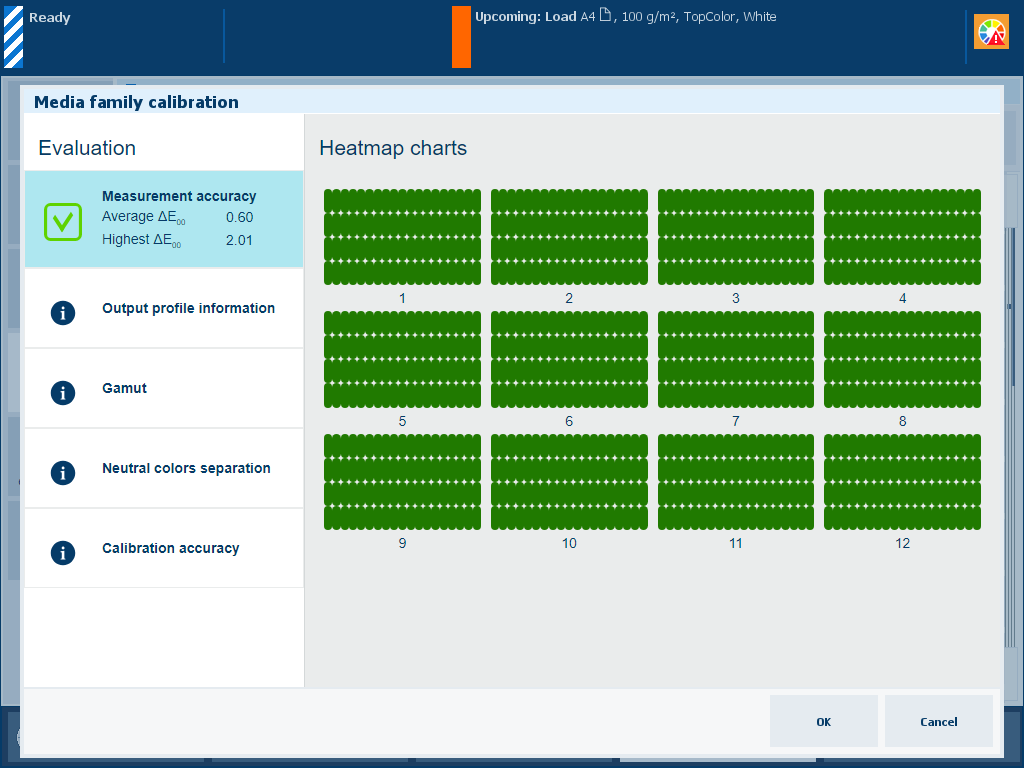 Feedback window of profile creation procedure
Feedback window of profile creation procedureWhen you see a green checkmark icon, touch [OK] to save the new calibration curves.
When you see a red cross icon, use the table below to evaluate the result. Then click [OK] to save the new calibration curves or [Cancel] to discard the results.
|
Feedback screen |
Remarks |
|---|---|

|
Description The ΔE values of the [Measurement accuracy] information are indicators for the accuracy by which the patches are printed and measured. The control panel displays a heatmap whose patch locations correspond with the printed chart. |
|
Evaluation
|
|
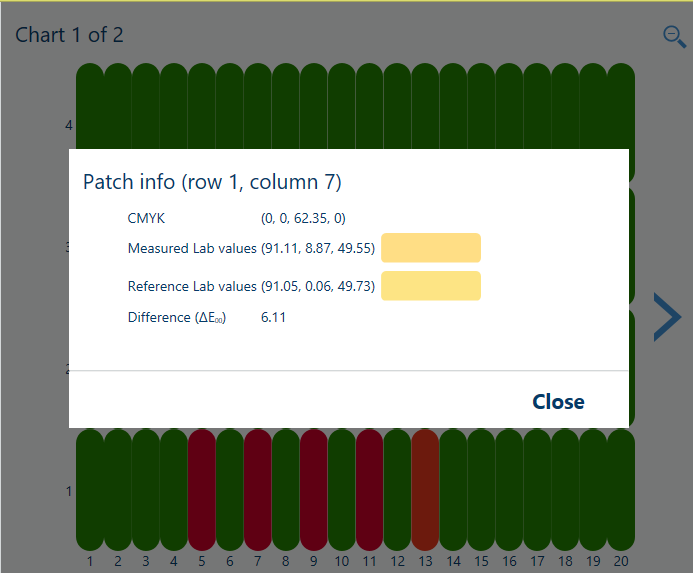
|
Options to improve color quality
|
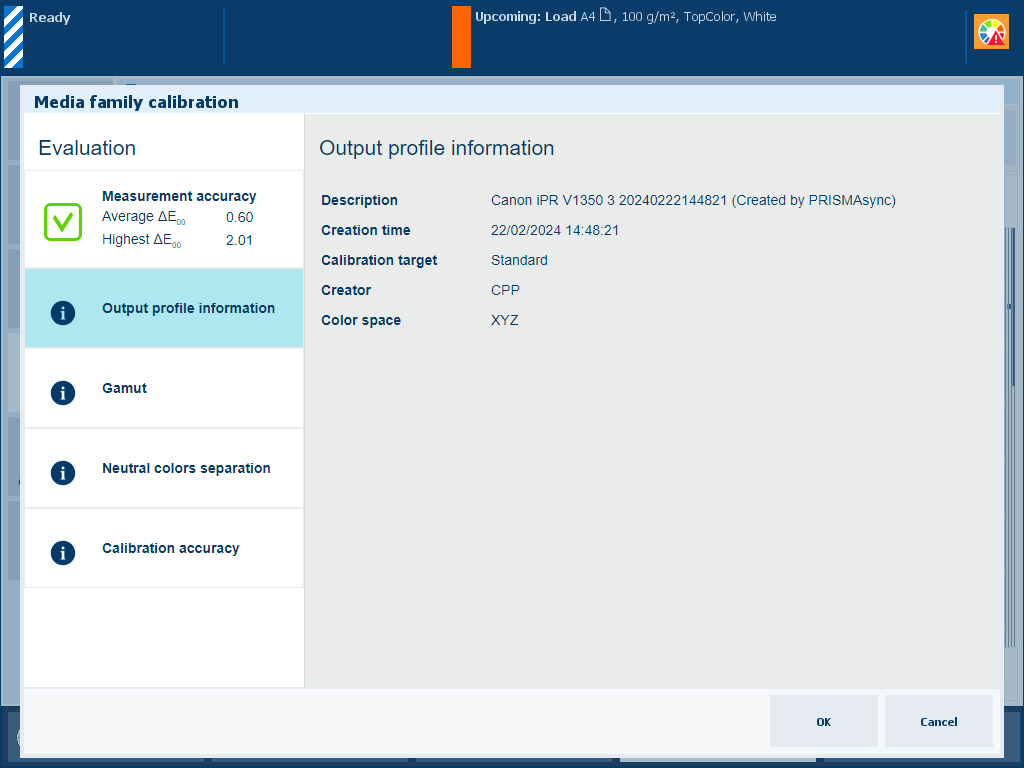
|
Description The [Output profile information] information shows the following characteristics about the output profile: description, creation time, calibration target, creator and color space. |
|
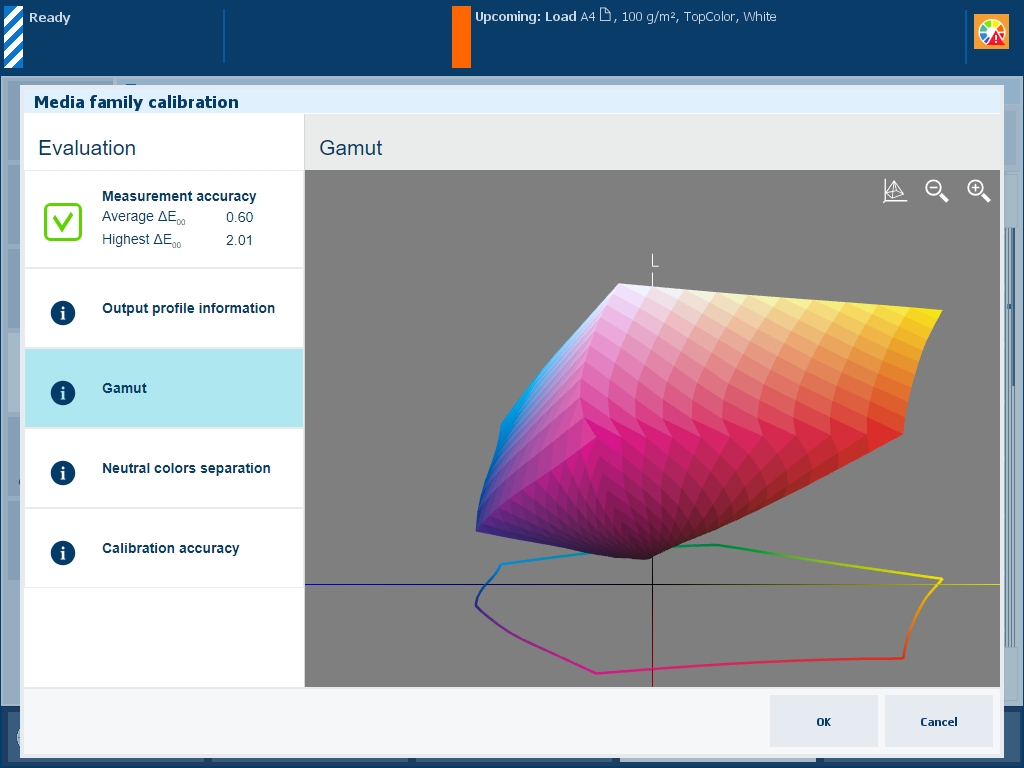
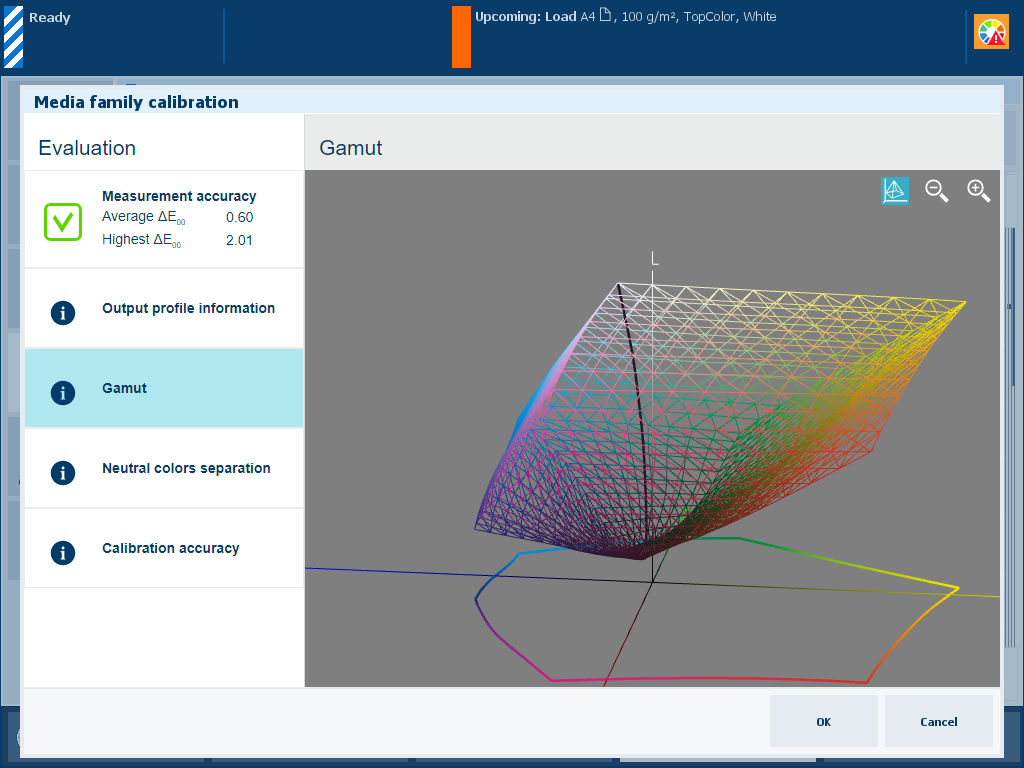
Description The [Gamut] information is an indication of the quality of the output profile. It is a visual representation of the color gamut that the printer can produce with the created output profile on the used media. Touch the wire frame
|
|
Evaluation
|
|
|
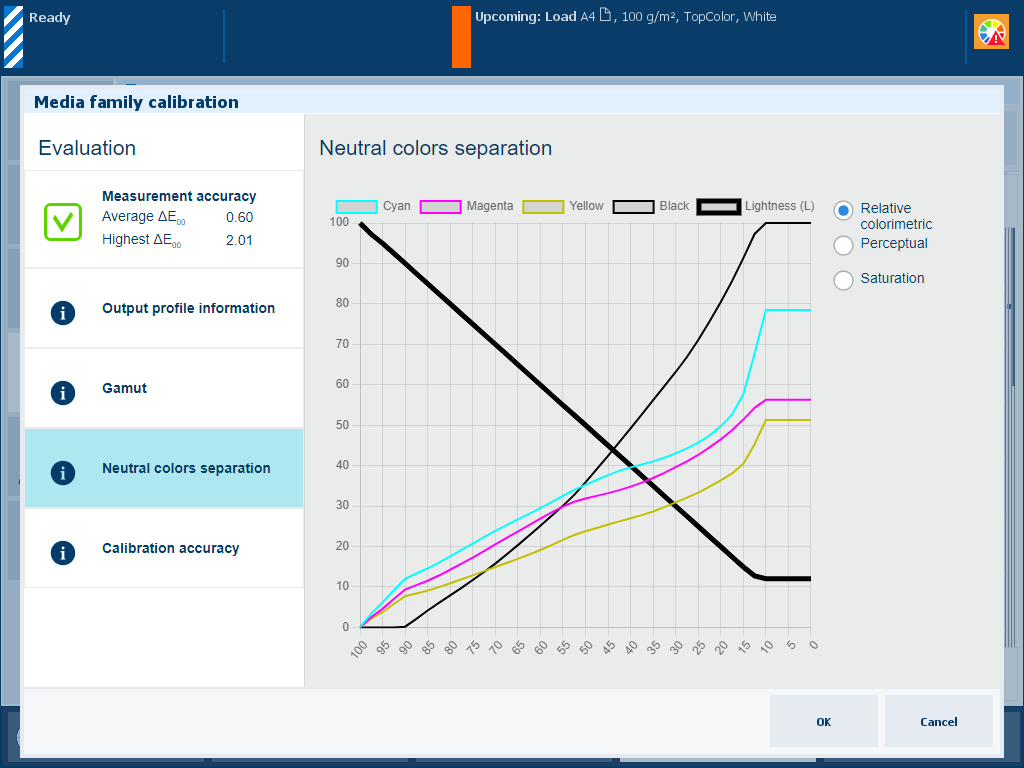
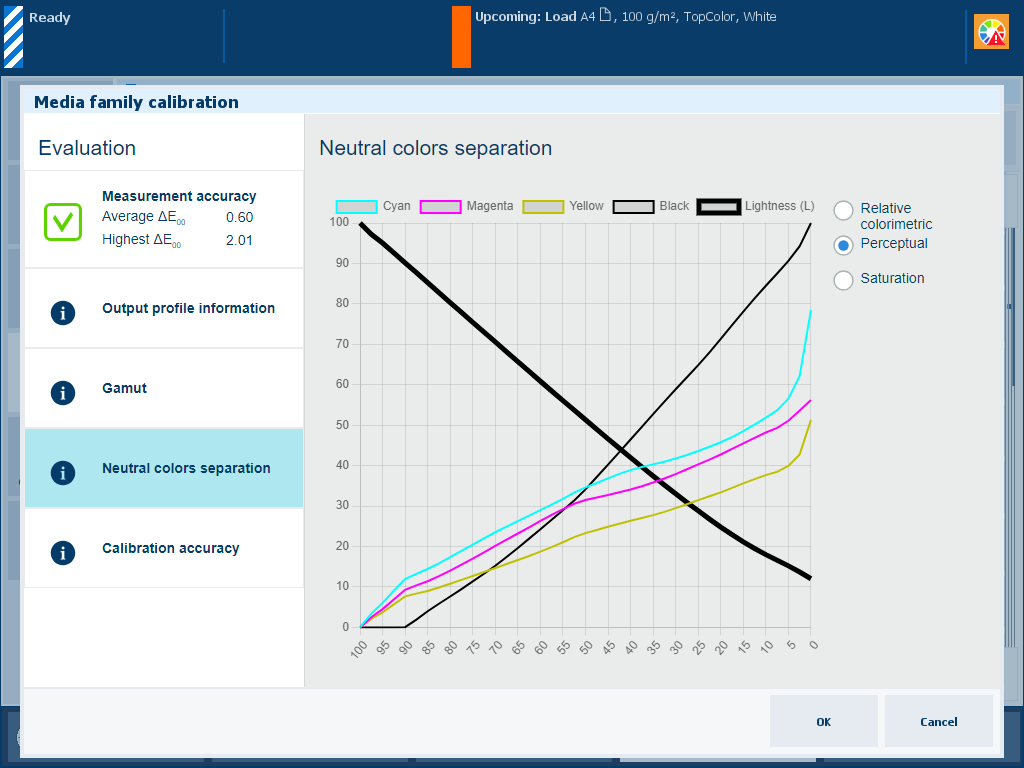
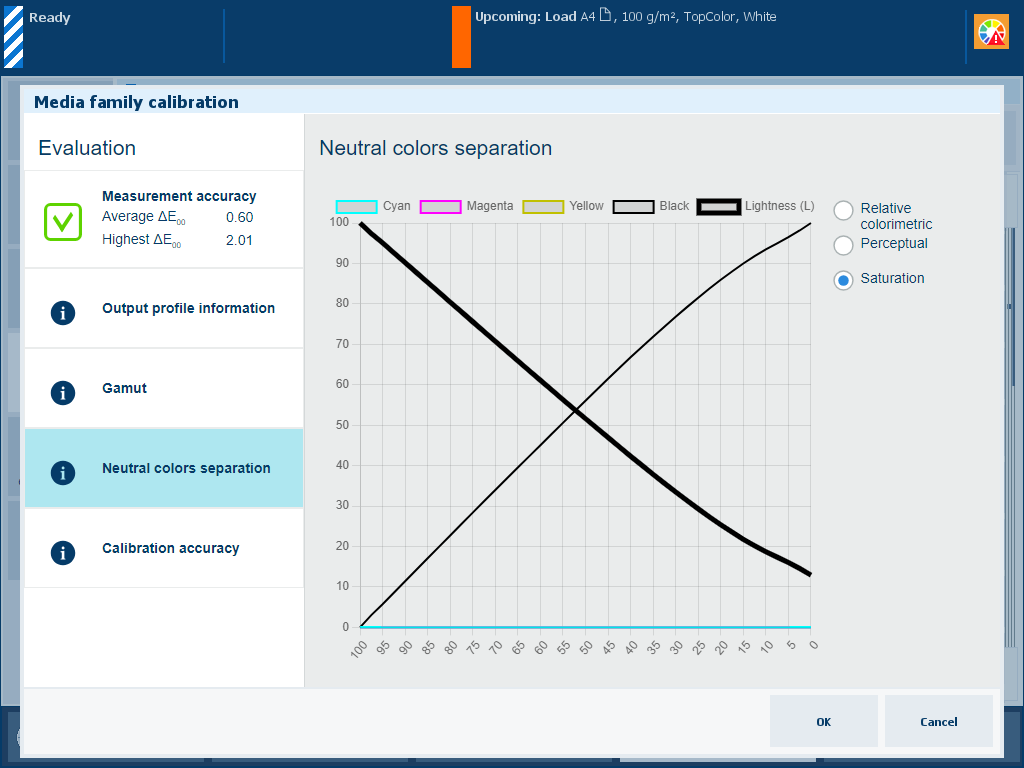
Description The thick black line of the [Neutral colors separation] graph shows how gray values are reproduced with the separate colors cyan, magenta, yellow and black (CMYK). Note that the darkest lightness value is on the left-hand side and the lightest value on the right-hand side. |
|
Explanation for [Relative colorimetric] selection The rendering intent [Relative colorimetric] reproduces true colors, for example for proofing applications and spot colors.
|
|
|
Explanation for [Perceptual] selection The rendering intent [Perceptual] reproduces contrasts in dark gray areas, for example for photos.
|
|
Explanation for [Saturation] selection The rendering intent [Saturation] reproduces saturated colors for example for business graphics.
|
|
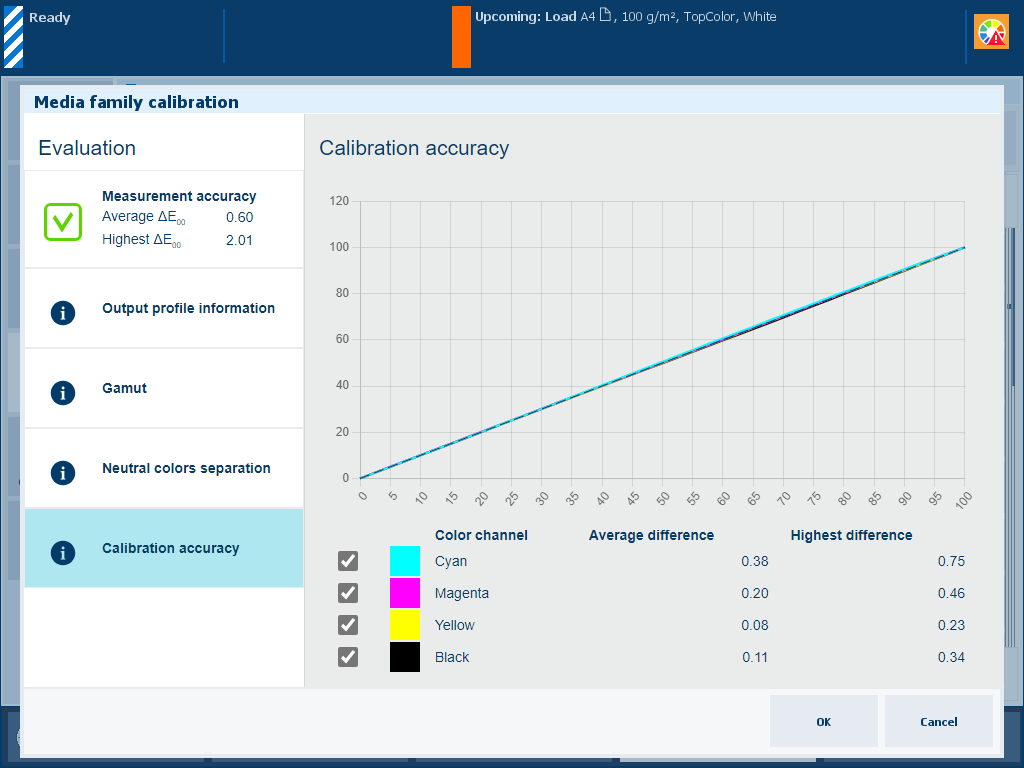
Description The percentage values of the [Calibration accuracy] information show how well the calibration procedure and output profile fit together. The graph shows per color channel how close the measured values meet the target values. |