

This topic contains the following instructions:
Define general rule properties
Define the rule endpoints
Define the [Connection mode]
Define the connection mode
Define the authentication method
Select [Internet Key Exchange protocol] (IKE)
Test the rule
Change the PRISMAsync Print Server default connection behavior
An IPsec rule defines what hosts have permission to IPsec according to the selected rule conditions. Moreover, IPsec rules can block all connections to one or more endpoints - via IPsec and all other protocols.
The IPsec configuration options apply to all IPsec connections that PRISMAsync Print Server establishes.
IPsec becomes active when at least one rule has been defined.
You can define maximum 20 PRISMAsync Print Server IPsec rules.
 Add IPsec rule
Add IPsec ruleGo to: .
 [IPsec communication] tab
[IPsec communication] tabClick [Add] or [Edit].
 [IPsec communication] menu
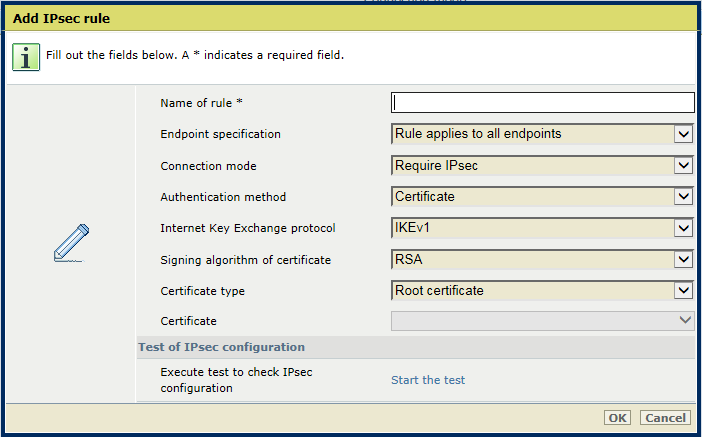
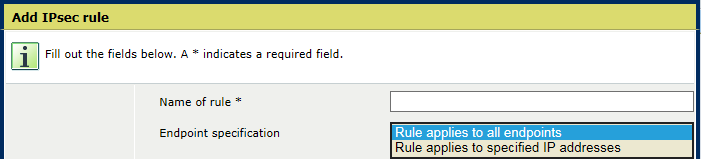
[IPsec communication] menuEnter a name in the [Name of rule] field.
 Add IPsec rule
Add IPsec ruleUse the [Endpoint specification] option to indicate if the rule applies to all endpoints or to specified IP addresses
Select [Rule applies to all endpoints] to create a rule for all connections
Select [Rule applies to specified IP addresses] to create a rule for which you specify the endpoints.
To specify the IP addresses, use the following guidelines.
You can use IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Separate multiple addresses with commas: 10.20.1.1,10.20.1.10.
Separate the beginning and the end of a range with a dash: 10.20.1.10-10.20.1.20.
You can add the subnet syntax: 10.20.2.0/24.
You can use pre-defined location names: LocalSubnet, DefaultGateway, DHCP, DNS, WINS.
When you use PRISMAsync Remote Manager an exemption rule for DNS is useful. The DNS server is essential to forward jobs from one PRISMAsync Remote Manager printer to another PRISMAsync Remote Manager printer.
 Add IPsec rule
Add IPsec rule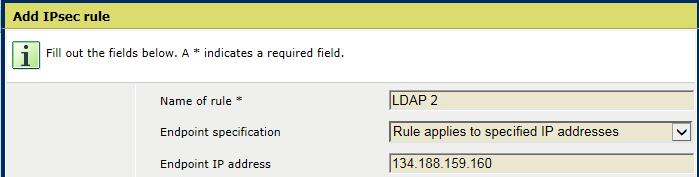 Add IPsec rule
Add IPsec ruleUse the [Connection mode] option to indicate how the rule options relate to the IPsec connection between the endpoints.
The diagram below can help to decide what connection mode is appropriate for specific endpoints.
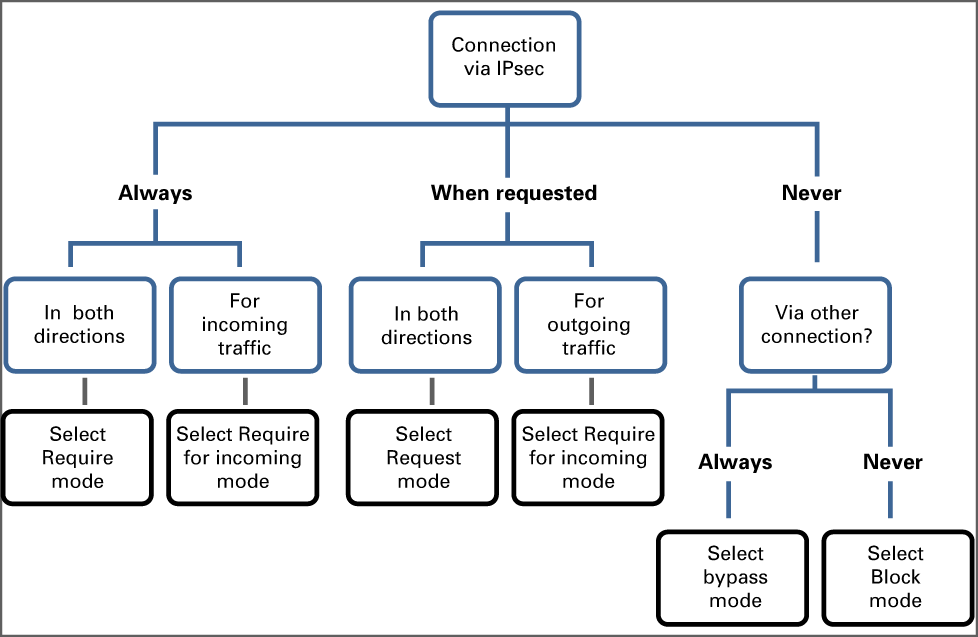 IPsec connection mode
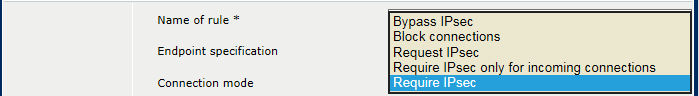
IPsec connection modePRISMAsync Print Server provides the following connection modes.
 IPsec connection mode
IPsec connection mode[Bypass IPsec] : define the endpoints for which connections can be established, but never via IPsec.
[Block connections] : define the endpoints for which no connections can be established. IPsec negotiations with the specified endpoints will not be initiated.
[Request IPsec]: define the endpoints for which IPsec is the preferred connection, but alternative connection protocols are also accepted.
[Require IPsec only for incoming connections] : define the endpoints for which IPsec is the required connection protocol for incoming traffic. For outgoing traffic, alternative connection protocols are also accepted.
[Require IPsec] : define the endpoints for which IPsec is the required connection protocol for incoming and outgoing traffic.
You are advised to first select and test the [Request IPsec] mode before you go to the [Require IPsec] mode.
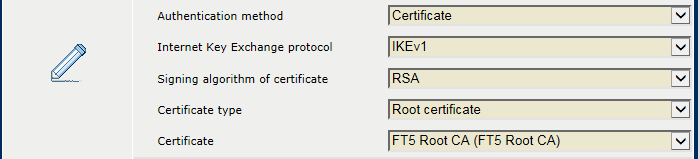
Use the [Authentication method] option to define how the endpoints must authenticate: [Certificate], [Pre-shared key] or [Certificate followed by pre-shared key].
When you select [Certificate] :
 Authentication method
Authentication methodCheck if the CA certificates of the endpoint or endpoints have been imported in the list of trusted certificates.
Use the [Signing algorithm of certificate] option to select the digital signature algorithm: [RSA], [ECDSA P256], [ECDSA P384].
 Signing algorithm
Signing algorithmUse the [Certificate type] option to select the type of CA certificate of the endpoint: [Intermediate certificate] or [Root certificate].
 Certificate type
Certificate typeUse the [Certificate] option to select the certificate from the PRISMAsync Print Server list of trusted certificates.
When you select [Pre-shared key] :
Use the [Pre-shared key] option to enter the key.
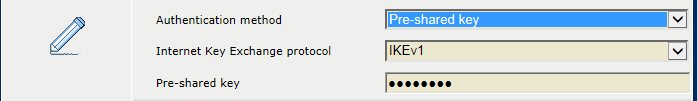 Pre-shared key
Pre-shared keyWhen you select [Certificate followed by pre-shared key] :
Specify the certificate and the pre-shared key as explained above.
Use the [Internet Key Exchange protocol] option to select the protocol: [IKEv1], [IKEv1 and AuthIP], [IKEv1 and IKEv2], [IKEv2].
 IKE protocol
IKE protocolClick [Start the test] of the [Test of IPsec configuration] option to check the authentication properties of the rule.
 Test the IPsec rule
Test the IPsec ruleBy default, PRISMAsync Print Server accepts host connections that are not secured by IPsec. You can invert this default behavior. Then, you only enable host communication that meets one or more rules. Therefore, you first create a block rule to deny all connections that impacts connections with and without IPsec. The other rules you create define what host are accepted, and under what conditions the connection must use IPsec.
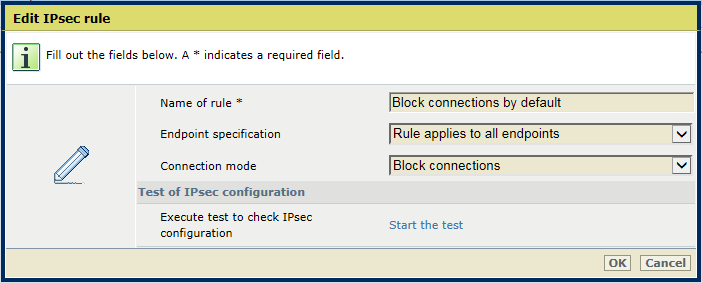 Edit IPsec rule
Edit IPsec ruleWhen more rules apply to the same endpoints, the priority mechanism of Windows takes effect. This means that:
The rule that has the most specific endpoint description is used. For example, a rule with one endpoint takes priority over a rule with an address range.
A restrictive rule takes priority over a permissive rule. A restrictive rule drops the connection when the IPsec negotiation fails. A permissive rule enables the communication to fall back to another connection if the IPsec negotiation fails.