

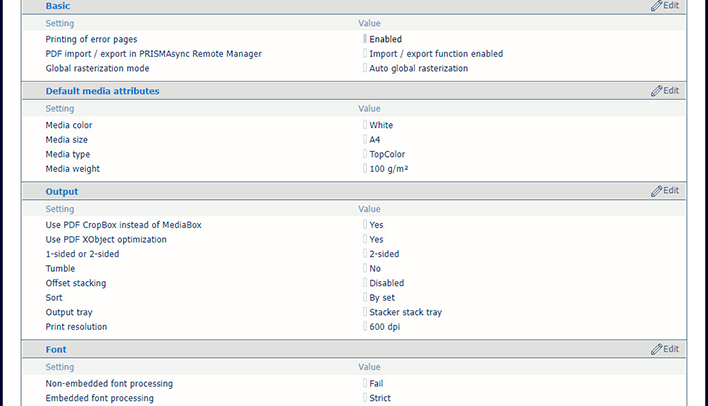
 Default [PDF] settings
Default [PDF] settingsOpen the Settings Editor and go to: .
 [PostScript], [PDF] and [PPML] tabs
[PostScript], [PDF] and [PPML] tabsClick [PostScript], [PPML] or [PDF].
In the [Basic] section, use the [Printing of error pages] setting to enable or disable the printing of error pages.
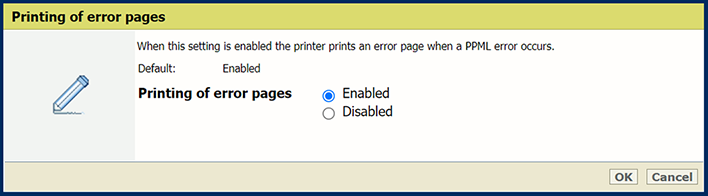 [Printing of error pages] setting
[Printing of error pages] settingIn the [Basic] section, use the [Job timeout] setting to define the job timeout. When the processing time of a PostScript job exceeds the set value, the printer prints - if enabled - an error page.
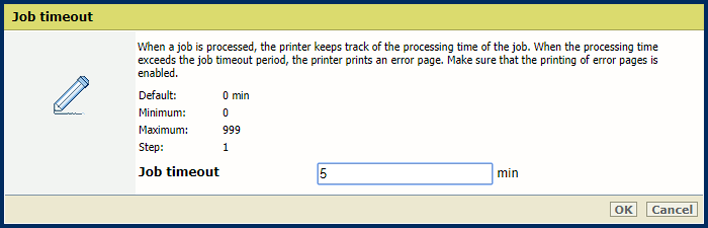 [Job timeout] setting
[Job timeout] settingIn the [Basic] section, use the [Page timeout] setting to define a page timeout. When the processing time of a PostScript page exceeds the set value, the printer prints - if enabled - an error page.
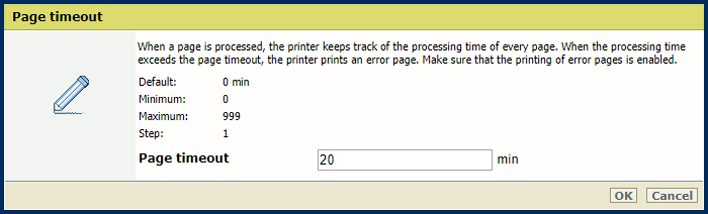 [Page timeout] setting
[Page timeout] settingUse the [Ejection of sheets due to setpagedevice command] setting to define if the printer must perform strict setpagedevice interpretations.
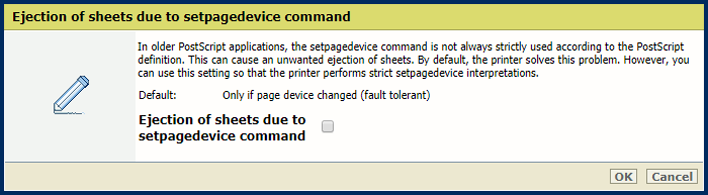 [Ejection of sheets due to setpagedevice command] setting
[Ejection of sheets due to setpagedevice command] settingUse the [PDF import / export in PRISMAsync Remote Manager] setting to enable the export and import of PDF files in PRISMAsync Remote Manager. This allows users of PRISMAsync Remote Manager to preflight, inspect, and edit PDF files with a PDF editor application.
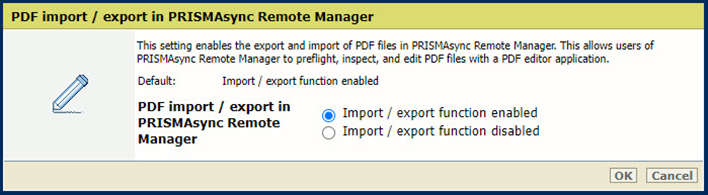 [PDF import / export in PRISMAsync Remote Manager] setting
[PDF import / export in PRISMAsync Remote Manager] settingUse the [Global rasterization mode] setting to modify the flattening process.
Select [Auto global rasterization] to automatically select the flattening algorithm (standard hybrid flattening or global rasterization) depending on page complexity.
Select [Forced global rasterization] to always use global rasterization.
The standard hybrid flattening algorithm is fast and performs well in most cases. Each region where objects overlap is flattened in a single color-blending operation. However, standard hybrid flattening can sometimes be too memory-intensive and lead to a crash, for example, when many objects on a page are stacked on top of each other. In such cases, it is recommended to use global rasterization instead. This algorithm uses pixel-to-pixel color blending.
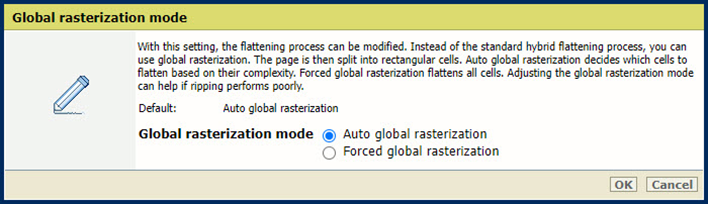 [Global rasterization mode] setting
[Global rasterization mode] settingIn the [Default media attributes] section:
Use the [Media color] setting to define the color of the default media. When you enter the color name in the English language, a sample of the color is automatically displayed in the media catalog. For other languages, enter the RGB value of the color.
Use the [Media size] setting to define the default media size.
Use the [Media type] setting to define the default media type.
Use the [Media weight] setting to define the default media weight.
In the [Output] section, use the [Use PDF CropBox instead of MediaBox] setting to use the PDF CropBox or the PDF MediaBox. The PDF MediaBox defines the size of the media used for printing.
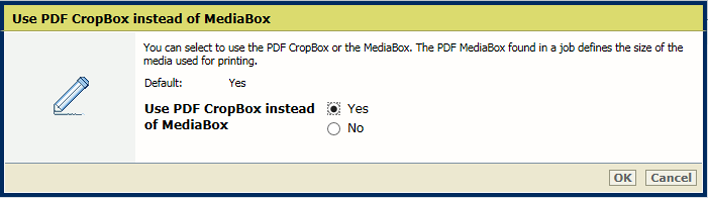 [Use PDF CropBox instead of MediaBox] setting
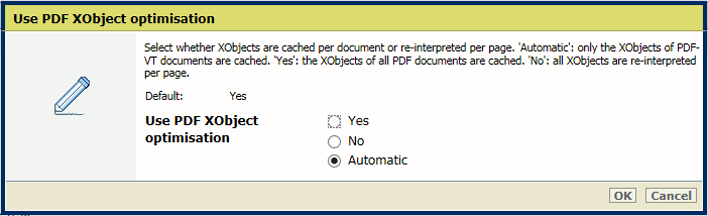
[Use PDF CropBox instead of MediaBox] settingIn the [Output] section, use the [Use PDF XObject optimization] setting to define how XObject objects are processed. XObject objects, such as background images, are defined only once in a PDF file.
[Automatic]: the XObject of PDF/VT jobs are cached.
[Enabled]: the XObject of every PDF job are cached.
[Disabled]: the XObject are re-interpreted per page.
 [1-sided or 2-sided] setting
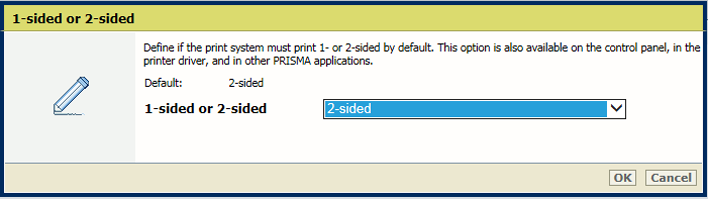
[1-sided or 2-sided] settingIn the [Output] section, use the [1-sided or 2-sided] setting to define if jobs are printed one- or two-sided.
 [1-sided or 2-sided] setting
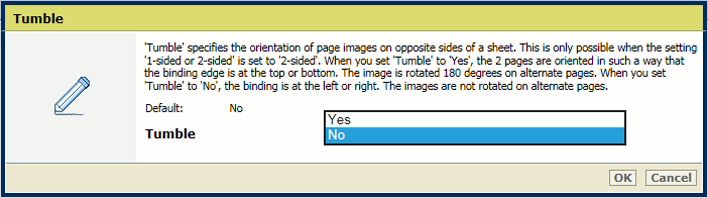
[1-sided or 2-sided] settingIn the [Output] section, use the [Tumble] setting to tumble two-sided documents that are bound at the top or the bottom edge. The tumble setting rotates the imposition of the back side 180 degrees.
 [Tumble] setting
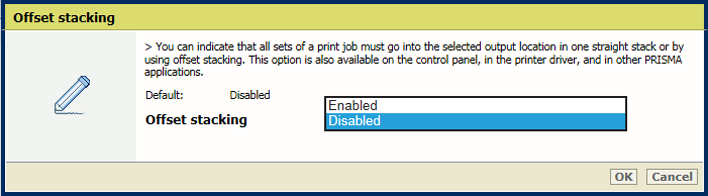
[Tumble] settingIn the [Output] section, use the [Offset stacking] setting to indicate if stacking occurs with or without an offset.
 [Offset stacking] setting
[Offset stacking] settingIn the [Output] section, use the [Sort] setting to define if sorting occurs by set or by page.
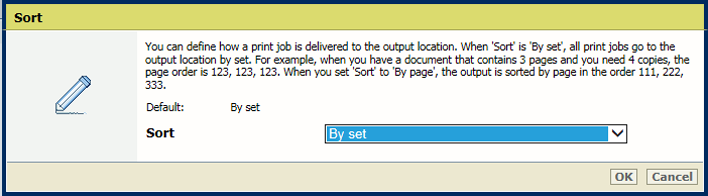 [Sort] setting
[Sort] settingIn the [Output] section, use the [Output tray] setting to select the output tray.
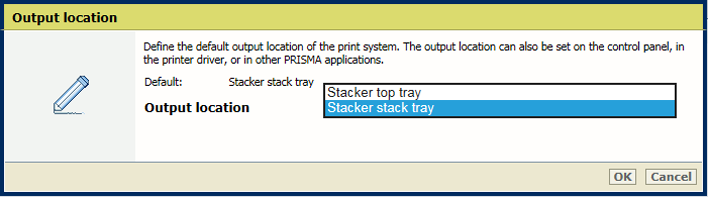 [Output tray] setting
[Output tray] settingIn the [Output] section, use the [Print resolution] setting to define the print resolution.
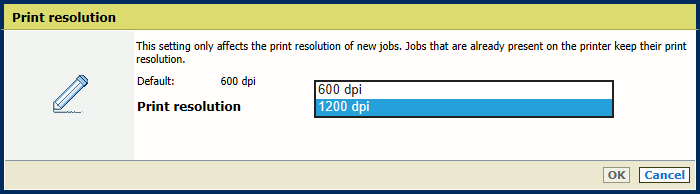 Print resolution
Print resolutionIn case of non-embedded fonts, PRISMAsync attempts to use the fonts that are available on the controller. If the required font is not available, there are two options.
If you select [Emulate font], the font is emulated based on the file metadata.
If you select [Fail], an error page is printed to inform you that a font is missing. For some products, it is necessary to enable the [Printing of error pages] setting.
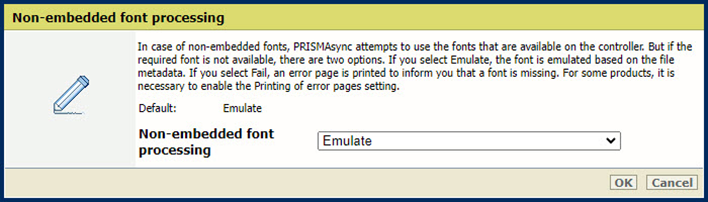 [Non-Embedded font processing] setting
[Non-Embedded font processing] settingTo define how corrupted embedded fonts are handled, use the [Embedded font processing] setting.
[Strict] font processing means that a corrupted font is immediately rejected and the print job is stopped.
[Best effort] font processing attempts to solve font corruption issues. However, this may result in formatting problems or blank spaces.
 [Embedded font processing] setting
[Embedded font processing] settingYou need to restart the system so that the changes can take effect. You have the option to restart now or at a later time. Keep in mind that delaying the restart results in inaccurate job previews.